How To Calculate BMI : How to Measure and Interpret Your Body Mass Index & How To Improve Your BMI
Discover how to calculate and interpret your Body Mass Index (BMI) with this comprehensive guide. Learn how to assess your weight and make informed decisions about your health.
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a commonly used tool to assess a person's weight and determine if they are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. This guide will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to calculate your BMI and interpret the results. By understanding your BMI, you can make informed decisions about your health and take necessary steps to maintain a healthy weight.
What is BMI and why is it important?
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a numerical value that is calculated using a person's height and weight. It is an important tool in assessing weight status and determining if someone is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. BMI is important because it provides a general indication of whether a person's weight is within a healthy range for their height. It can help identify potential health risks associated with being underweight or overweight, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. By knowing your BMI, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy weight and reduce your risk of developing these health conditions.
How to calculate BMI.
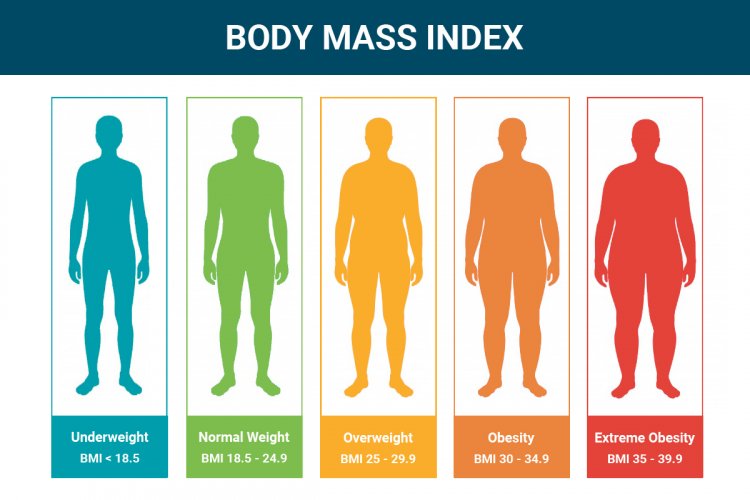
Calculating your BMI is a simple process that involves using your height and weight measurements. To calculate your BMI, you can use the following formula: BMI = weight (in kilograms) / (height (in meters))^2. First, you need to convert your weight from pounds to kilograms. To do this, divide your weight in pounds by 2.2046. Next, you need to convert your height from inches to meters. To do this, divide your height in inches by 39.37. Once you have your weight in kilograms and your height in meters, you can plug these values into the BMI formula. Divide your weight in kilograms by the square of your height in meters. The resulting number is your BMI. After calculating your BMI, you can interpret the results using the following categories: - Underweight: BMI less than 18.5 - Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 - Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9 - Obese: BMI 30 or higher Keep in mind that BMI is a general indicator and does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or body composition. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment of your weight and health
Understanding BMI categories and what they mean.
BMI categories are used to classify individuals into different weight ranges based on their Body Mass Index. Understanding these categories can help you assess your weight and make informed decisions about your health.
- Underweight: A BMI less than 18.5 is considered underweight. This may indicate that you are not getting enough nutrients and may be at risk for health problems such as weakened immune system, osteoporosis, and fertility issues.
- Normal weight: A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal weight. This range is associated with the lowest risk of developing weight-related health problems. However, it's important to note that BMI does not take into account factors such as muscle mass, so it may not be the most accurate measure for athletes or individuals with high muscle mass.
- Overweight: A BMI between 25 and 29.9 is considered overweight. This range indicates that you may have excess body weight, which can increase your risk for health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
- Obese: A BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese. This range indicates a significantly higher risk for weight-related health problems. Obesity is associated with an increased risk for conditions such as heart disease, stroke, certain types of cancer, and sleep apnea.
It's important to remember that BMI is just one tool used to assess weight and health. It does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or body composition. For a comprehensive assessment of your weight and health, it's best to consult with a healthcare professional.
The limitations of BMI as a measure of health.
While BMI can be a useful tool for assessing weight and health, it does have its limitations. One of the main limitations is that it does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or body composition. This means that individuals with high muscle mass, such as athletes or bodybuilders, may have a higher BMI even though they have a low body fat percentage and are in good health. On the other hand, older adults or individuals with low muscle mass may have a lower BMI even though they have a higher body fat percentage and are at risk for health problems. Additionally, BMI does not differentiate between fat distribution in the body, which can also impact health. For example, carrying excess weight around the waist (central obesity) is associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular disease and other health problems. Therefore, while BMI can provide a general indication of weight-related health risks, it should not be the sole determinant of an individual's overall health. It's important to consider other factors such as body composition, waist circumference, and overall lifestyle when assessing health.
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on an individual's weight and height. It is commonly used to assess whether a person has a healthy body weight for their height. The BMI formula is as follows:
BMI = weight (in kilograms) / (height (in meters))^2
Alternatively, if you prefer to use pounds and inches:
BMI = (weight (in pounds) / (height (in inches))^2) * 703
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to calculate BMI using the metric system:
-
Convert your weight from pounds to kilograms if necessary. Divide your weight in pounds by 2.2046 to get the weight in kilograms.
-
Convert your height from inches to meters if necessary. Divide your height in inches by 39.37 to get the height in meters.
-
Square your height by multiplying it by itself.
-
Divide your weight in kilograms by the squared height in meters.
The result will be your BMI, which indicates which category your body weight falls into, such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Keep in mind that BMI is a general indicator and does not take into account factors such as muscle mass or body composition, so it may not be an accurate measure for everyone. It is always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional for a more comprehensive assessment of your health and body weight.
-
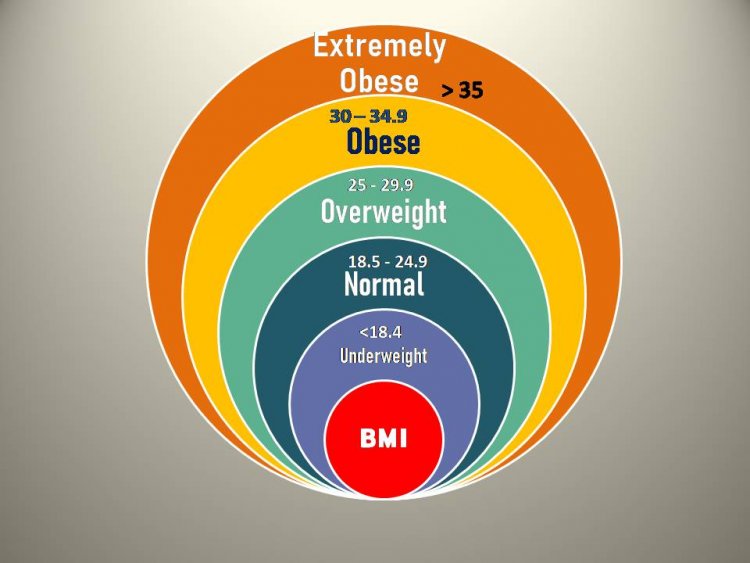
Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- This range indicates that a person may be underweight, which can have its own health implications. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
-
Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Falling within this range suggests that a person has a healthy body weight for their height. It's generally associated with lower health risks compared to other BMI categories.
-
Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- This range indicates that a person may be overweight, which can increase the risk of various health issues, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. However, it's important to consider other factors like body composition and overall health.
-
Obesity:
- Class I: BMI between 30 and 34.9
- Class II: BMI between 35 and 39.9
- Class III (severe obesity): BMI 40 or higher
- These ranges represent different degrees of obesity, with higher BMI values indicating a greater risk of obesity-related health problems.